Understanding the basics of Photovoltaics in simple words
The Earth receives an enormous amount of solar energy from the sun, estimated to be approximately 173,000 terawatts daily.
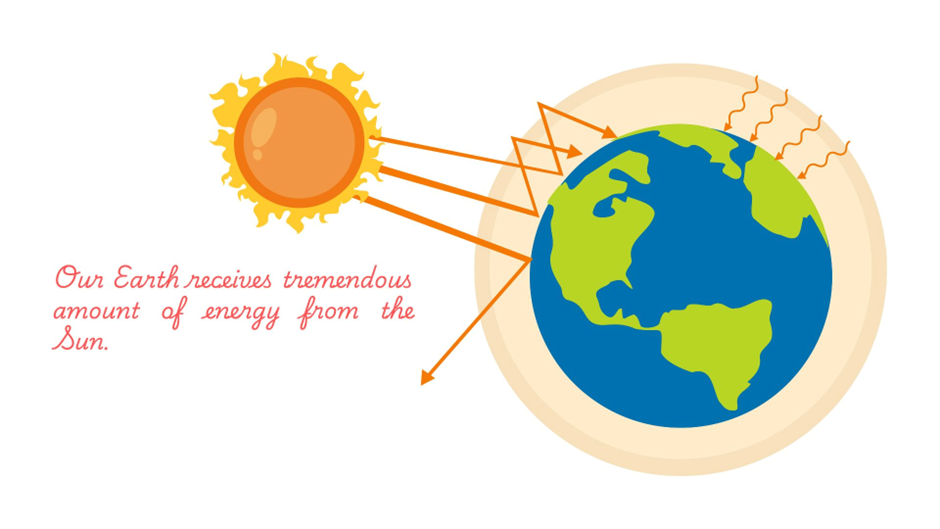
This energy reaches the Earth through electromagnetic radiation, primarily visible light, ultraviolet light, and infrared radiation.
The average distance between our earth and the sun is 150 million km.
The sunlight covers this large distance in very little time of 500 seconds (8 minutes and 20 seconds) with an incredible velocity of 3 lakh km per second.
The sun you observe daily is a picture of it 8 minutes and 20 seconds ago.
This speed is almost 10 million times more than the speed of sound in air.
Potential of Solar Energy
The solar energy that reaches the Earth is many thousand times more than the total energy consumption of the entire planet, highlighting its vast potential as a renewable energy source.
However, not all of this energy is harnessed.
The significant portion is reflected into space by the atmosphere and clouds.
While the rest is absorbed by the Earth’s surface and oceans, driving weather patterns and providing the warmth necessary for life.
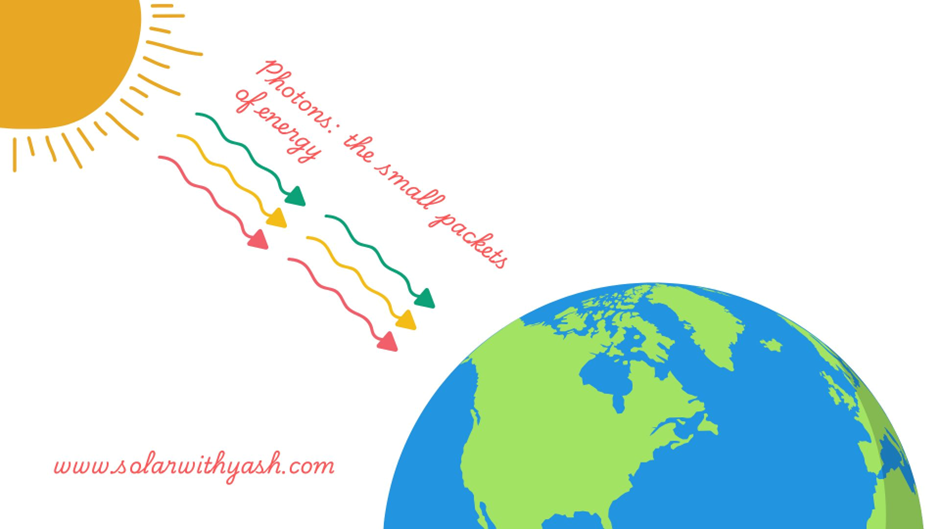
The Photons
The sunlight consists of small packets of energy called Photons.
What is Photovoltaics?
And we can harness this energy to produce electricity.
And one way is through Photovoltaics (PV)
It is a technology that converts sunlight directly into electricity using semiconducting materials.
When these photons of light fall on photo-sensitive material like silicon. The electrons in the outermost shell get excited.
These electrons jump from the valence band into the conduction band. Now they are free to move and hence constitute an electric current.

We can use this electricity to meet our various energy needs.
You can use it for powering EVs, running electrical appliances, and many other things.
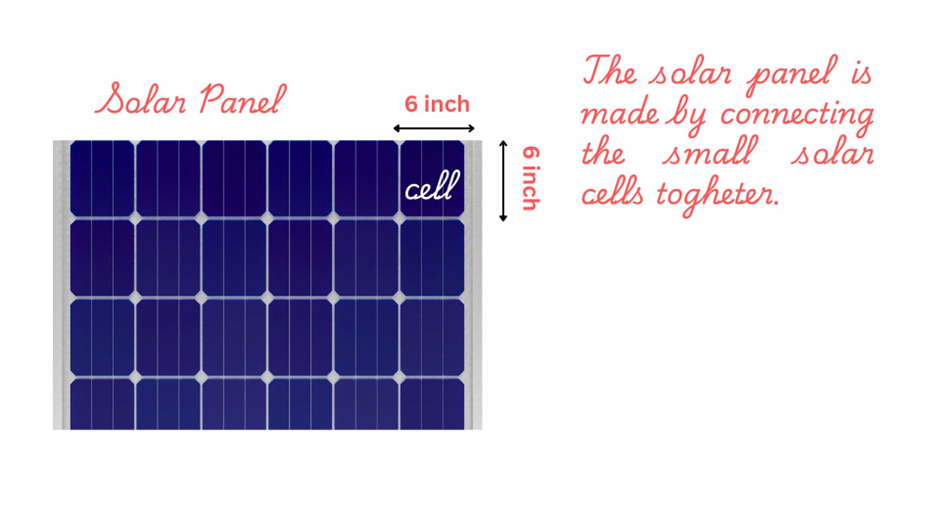
Solar panel: the interface of photovoltaics
The single solar cell is small in size of 6 inches by 6 inches.
A typical solar cell produces an open-circuit voltage of about 0.5–0.6 volts. This is the maximum voltage a cell can produce without any power draw.
When a cell is under load, the voltage is about 0.46 volts, and it generates a current of about 3 amperes.
This energy is very small to make it use in our daily lives.
Therefore, these solar cells are joined and enclosed together in the form of a solar panel.
The solar panels now produce enough electricity to meet our daily energy needs.
Benefits of Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics, the technology that converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar cells,
It offers numerous benefits that are increasingly recognized in the quest for sustainable energy solutions.
Firstly, photovoltaics provides a clean, renewable source of energy that significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the fight against climate change.
Unlike fossil fuels, solar power does not produce air pollutants or carbon dioxide during operation.
Additionally, solar energy is abundant and virtually inexhaustible, ensuring a stable energy supply that is not subject to the price volatility associated with fossil fuels.
Photovoltaics also offer economic advantages, including the potential for significant energy cost savings for homeowners and businesses, as well as job creation in the manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of solar panels.
Moreover, solar power systems can be deployed at various scales, from small residential setups to large utility-scale installations, providing flexibility and energy independence.
In addition, the solar photovoltaics technology is very mobile. It can power electric/electronic devices under the sun be it your car, RV, boat, or spacecraft.
Another advantage of solar photovoltaics technology is that it can be installed on any terrain on the earth like mountains, deserts, or water where it is very difficult for the grid electricity to reach there.
Lastly, advancements in photovoltaic technology continue to improve efficiency and reduce costs, making solar energy an increasingly accessible and appealing option worldwide.
Future of Photovoltaics
The future of photovoltaics holds immense promise as the world increasingly shifts towards sustainable energy solutions. Advances in solar technology are making photovoltaic panels more efficient, affordable, and versatile. Emerging technologies, such as Perovskite solar cells, Mono-PERC technology, Half-cut solar panels, and bifacial panels, have made solar photovoltaics more efficient than ever.
Today we see solar panels having absorbing more sunlight per square meter than before and reaching efficiencies as high as 23%. The bifacial solar panels even absorb the reflected light from their rear side.
With ongoing research, the development of lightweight and flexible solar panels could revolutionize portable and wearable energy solutions. As governments and industries invest in renewable energy infrastructure, photovoltaics will likely play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and promoting energy independence, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable future.